
Hickory (Carya spp.)

Hickory (Carya spp.) is composed of at least 16 species native to Asia, Central America and North America. The word carya is from the Greek name for nut. This group can be split into the true hickories and the pecans based on microanatomy.
Grades Available: Sel/Btr, #1 Common, #2 Common
Sizes Available: 4/4
Distribution: Eastern to mid-western United States.
The Tree: Hickory trees can reach a height of 140’ ft, with a diameter of 4’ ft.
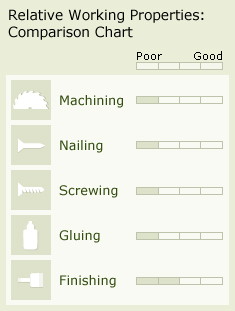
General Wood Characteristics: The sapwood of hickory is white, tinged with brown, while the heartwood is pale to reddish brown. The wood is known for its strength and shock resistance. It is difficult to dry or season. It rates above average in most working properties except in shaping and nail-holding ability. The wood of pecans is rated slightly below that of true hickories.
Working Properties: Hickory is considered difficult to machine and glue. It holds nails well, but it tends to split. It is susceptible to bird peck.
Durability: Extremely resistant.
Uses: Tool handles, furniture, cabinetry, ladder rungs, dowels, sporting goods (including baseball bats, skis and archery equipment), flooring, veneer, plywood, fuelwood and charcoal.

